What is ITIL?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) framework is a set of best practices and processes designed to help ensure the alignment of IT services to business goals. It is used by organizations to manage the end-to-end lifecycle of their IT systems and services and improve the efficiency with which they meet their requirements as they evolve over time.
ITIL is an essential tool in the modern digital workplace and provides a clear structure for enabling digital transformation.
The ITIL Framework helps an organization to define its IT service, align services with customers' needs, and produce a clear model for ongoing success. It is used to improve core IT service processes and is flexible to each organization's unique requirements.
BRIEF HISTORY OF ITIL
The need of an efficient IT framework came from the British Government at the end of the 80s. The Office of Government Commerce (formerly the Central Computer and Telecommunication Agency – CCTA) developed the first version of ITIL. This was very different from the existing framework.
During the 90s and 2000s, the framework spread through many government agencies and companies in Europe, in the US and all around the world.
In 2001 ITIL Version 2 was released, and this has been updated to ITIL v3 in 2007. This latest version took a more lifecycle approach to managing services, with a greater emphasis on IT-business integration.
ITIL v3 was updated in 2011, without changing the version number, since the concepts underling the framework remained the same.
The last and most update version of ITIL framework is ITIL 4, launched in 2019 by the owner AXELOS. This edition has changed the current ITIL content to better reflect today's business and IT environments, while maintaining flexibility to ensure it complements other approaches.
WHAT’S NEW WITH ITIL 4?
ITIL 4 refocuses on customer experience and digital transformation. It addresses real-world problems of modern IT governance, such as cloud-based services or machine learning. Digital technologies are changing rapidly, and ITIL 4 provides the tools and insights to respond and mitigate risk. The ITIL framework helps companies create efficient and high-quality environments and deliver IT services quickly. It is a vehicle for change because organizations can also use it to understand and implement new ways of working, such as DevOps, Lean, and Agile.
It ensures that IT services are aligned with business aims using the Service Value System principle, which links all of a business’ IT activities to organization's goals. ITIL 4 introduced the Service Value Chain system, which is a flexible model for planning the customer journey.
ITIL 4 consists of 34 different practices focused on improving technology management, service management and general management. The organization receives processes and functions for all service delivery areas, including risk management, people development and asset development.
ITIL 4 KEY CONCEPTS
ITIL has several key principles that are realized through five core components. The key concepts of ITIL are:
- Deliver the maximum value to customers
- Optimize resources and capabilities
- Offer services that are useful and reliable
- Plan processes with specific goals in mind
- Define roles clearly for each task
ITIL 4 GUIDING PRINCIPLES
The seven guiding principles are the practical basis of ITIL. From the update from ITIL v3 to ITIL 4, also these have been changed and adapted to the modern needs of IT environments. The 7 guiding principles of ITIL 4 are:
- Focus on value
- Start where you are
- Progress iteratively with feedback
- Collaborate and promote visibility
- Think and work holistically
- Keep it simple and practical
- Optimize and automate
ITIL 4 MANAGEMENT PRACTICES
ITIL 4 defines 34 management practices to adopt modern organizational dynamics. It takes into account the overall dynamics of the current organizational scenario, such as innovation, speed to market, rapid response to market dynamics, dynamic expansion of resources, etc. This requires proper management practices for services, projects, products, design, transition, build, test, delivery and support by adapting and adapting to dramatically changing scenarios.
A management practice can be defined as a set of organizational resources dedicated to performing work or achieving goals, and they fall into three categories:
- 14 General management practices - applicable across the organization for the success of business and services provided by the organization.
- 17 Service management practices - applicable for specific services being developed, deployed, delivered and supported in an organization environment.
- 3 Technical management practices - adapted from technology management domains for service management purposes by expanding or shifting their focus from technology solutions to IT services.
ITIL FOUR DIMENSIONS
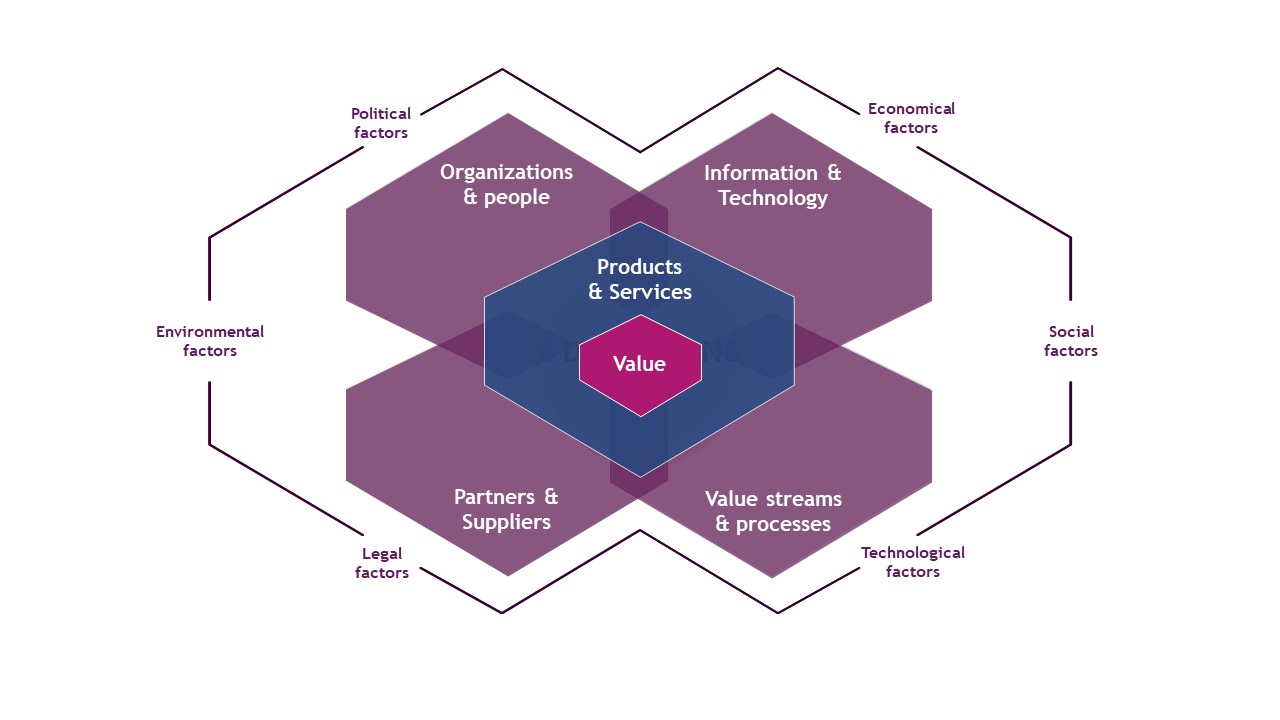
ITIL 4 has introduced four dimensions to be considered when delivering a service or product.
The dimensions ensure that the whole organization is considered, avoiding inefficient processes. ITIL 4 exhorts companies to map the four dimensions every time they design a service or product, while providing a framework for planning at a strategic level.
The four dimensions of ITIL 4 are:
- Organizations and People — This dimension focuses on the structure and leadership of the organization and the people involved in all aspects of ministry. This includes suppliers, customers, employees and managers. Organizations should consider how the team is connected, the level of education, and the type of organizational culture.
- Information and Technology — This dimension describes the tools, technologies and information required to support product delivery and IT governance and management. Considerations may include the capabilities and capacity to support the Services and the technology required for the Services.
- Partners and Suppliers — This element focuses on external suppliers and partners who help the company deliver its products and services. Comparing in-house and outsourced capabilities is an important part of this dimension. Businesses should consider and compare outsourcing costs, reliability, performance and capacity.
- Value Streams and Processes — This dimension is about how services and products are delivered. ITIL 4 introduces the concept of a service value chain, the operating model for delivering a service or product. The service value chain will be explored in more detail later in this article, but it can be used for incident response and product development.
THE SERVICE VALUE CHAIN
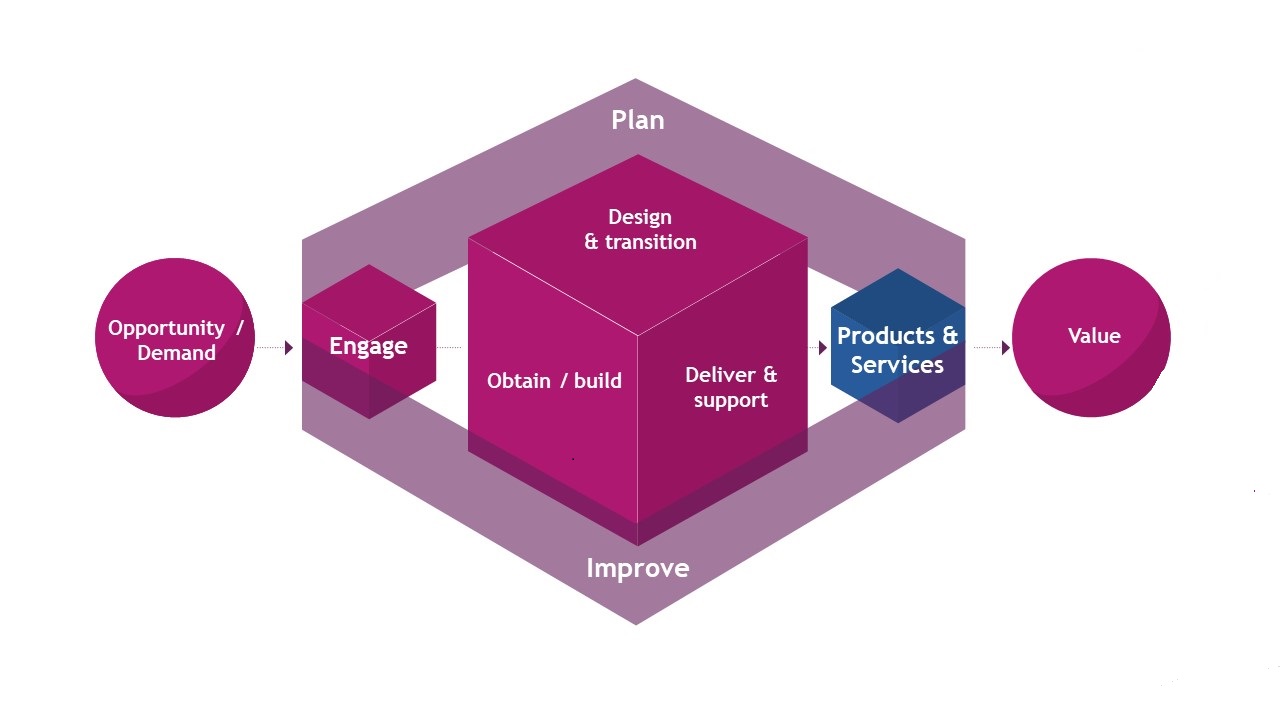
A major aspect of ITIL 4 is the introduction of the service value chain, a service delivery model. It focuses on the concept of value streams and replaces the service lifecycle system in ITIL 3.
A value stream is the journey from receiving an inquiry (or demand) to delivering a product or service (or value). In this case, the model is based on six flexible activities that can be rearranged to create value streams for specific purposes. It's very flexible because the value stream doesn't have to be linear. The sequence of activities can be dynamically adapted to the needs. For example, create an incident response process as part of your risk management strategy.
Of course, the service value chain brings together different areas of the entire organization with IT services as the link. This concept is an integral part of ITIL 4 because each activity can leverage procedures or practices described elsewhere in the framework. It promotes a holistic approach to advanced IT governance that enables informed strategic planning.
The six activities found within the Service Value Chain are:
- Engage — Engage with stakeholders to understand their needs. The aim is to forge good stakeholder relationships and understand their service requirements.
- Plan — Understand the direction, current status, and required improvements across the organization, services, and products.
- Improve — Achieve continuous improvements in services. Use the Service Value Chain to improve processes across all areas of the organization.
- Design and Transition — Ensure that the cost and quality of services meet the expectations of stakeholders.
- Obtain or Build —Ensure individual components of services are reliably available.
- Deliver and Support — Meet agreed expectations by delivering services and support.
HOW TO GET ITIL CERTIFIED?
ITIL 4 certification scheme provides a modular approach to acquiring competencies in the ITIL framework, comprising a set of qualifications based on various aspects of ITIL best practices, with varying degrees of depth and detail. Each module has an exam to demonstrate acquired skills and lead to certification.
Popular ITIL 4 courses and exams




Contact form

